
EXCEL DEBIT CREDIT RUNNING BALANCE HOW TO
Most Excel users do not know how to use or create named ranges. Notice that unlike OFFSET, Excel highlights cell F14 (the cell that prev_balance is referring to). Named ranges can make formulas easier to understand. Not familiar with named ranges? Check out the references listed at the end of this article to learn more. The named range was created using a relative reference, so when the running balance formula is copied down, prev_balance will always refer to the cell immediately above the current cell, even if you insert, delete, or move the rows. In this example, I've created prev_balance as a named range that refers to the cell immediately above the current balance. When you create a named range via Formulas > Define Name, you can use a relative reference like =F14 (no dollar signs) instead of an absolute reference like =$F$14. Solution #2 - Create a running balance using a Relative Named Range This particular use is very efficient, so it likely won't cause a problem unless you have a lot of other inefficient formulas that depend on the results of the OFFSET formula. OFFSET is a volatile function, which means it re-evaluates every time the worksheet is recalculated. Notice that in the image above, the OFFSET formula highlights the reference (cell F15) rather than the cell that OFFSET refers to (cell F14). OFFSET can make formulas difficult to understand. However, if you only use Excel, you might try Solution #2. The need for compatibility is one of the main reasons I use OFFSET in many of my templates. OFFSET is compatible with Google Sheets and OpenOffice. To see the OFFSET function used within functioning templates, take a look at the Checkbook Register and Credit Account Register, both of which include a running balance. You can insert, delete and move rows and the balance formula will always reference the cell above the current balance. The OFFSET function does not directly reference cell F14, so if you delete row 14, no problem. To refer to the previous balance, we can use the current balance (F15) as the reference and use -1 for the offset rows and 0 for the offset columns like this: =OFFSET(F15,-1,0). Syntax: = OFFSET( reference, rows, columns,) The OFFSET function allows you to create a reference by specifying the number of rows and columns offset from a particular reference. Solution #1: Create a Running Balance using the OFFSET Function There are two fairly simple solutions for creating a robust running balance that don't break when you insert, delete or move rows. So, you need to use formulas that don't cause hidden or hard-to-detect errors. If you are designing a spreadsheet with a running balance, it's likely that you or somebody else may want to insert, delete, or move rows.


If I have an error in a spreadsheet, I would much rather see a glaring #VALUE! or #REF! error than have errors I can't see. In fact, the running balance is wrong in both rows 2 and 3, because the formulas are not referencing the correct previous balance. The scary thing about this example is that there is no obvious indicator of the errors. In this example, row 3 was cut and inserted above row 2. Problem #3: Moving a Row Causes Hard-to-detect Errors It isn't wise to rely on the error checking feature because it doesn't catch all errors. In this case, a little green triangle indicates an inconsistent formula. The error checking feature in Excel was designed to help identify these types of errors. The problem is that the balance formula in row 3 is still referencing the balance from row 2. In this example, a new row was inserted above row 3 and the balance formula was then copied down. Problem #2: Inserting a Row Causes an Incorrect Running Balance While annoying to fix, it's not as scary as the errors that are harder to detect. This error is very obvious, and can be fixed fairly easily by fixing the balance formula in row 3. All dependent formulas also contain #REF! errors. The balance formula in row 3 now contains a #REF! error because the reference to the balance in row 2 was deleted.
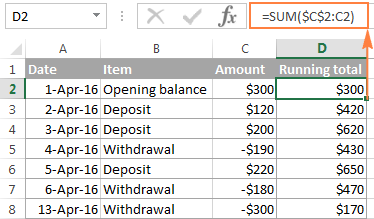
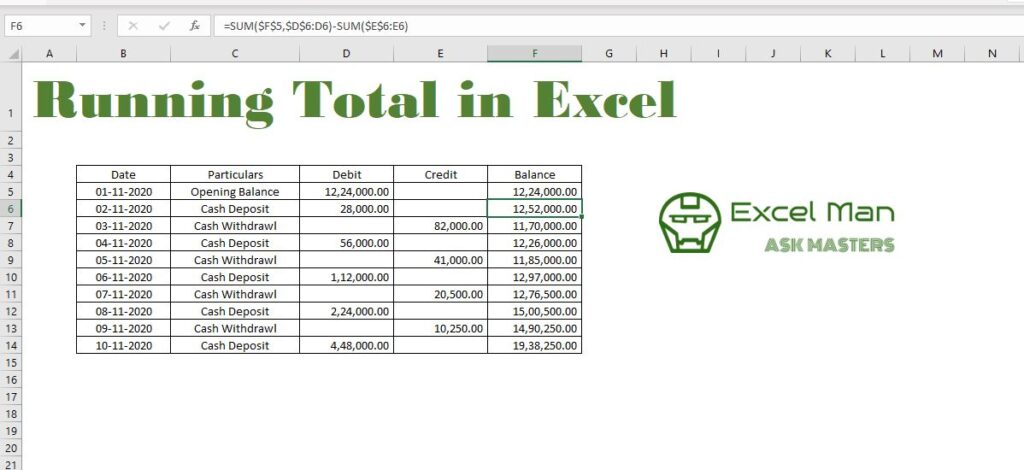
Problem #1: Deleting a Row Causes a #REF! Error Another approach is to leave a blank row underneath the columns labels, or use the first row to enter the carry over balance instead of using a formula. NOTE Why use SUM instead of =D15-E15+F14? Answer: The formula in the first row would lead to a #VALUE! error because of trying to add a text value (=5-1+"Balance").


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
